Coal, a fossil fuel that has been a cornerstone of human civilization for centuries, remains a vital component of the global energy mix. Despite its contributions to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation, coal continues to play a significant role in powering homes, industries, and transportation systems worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the multifaceted world of coal, exploring its uses, types, pollution effects, and fascinating facts.
What is Coal?
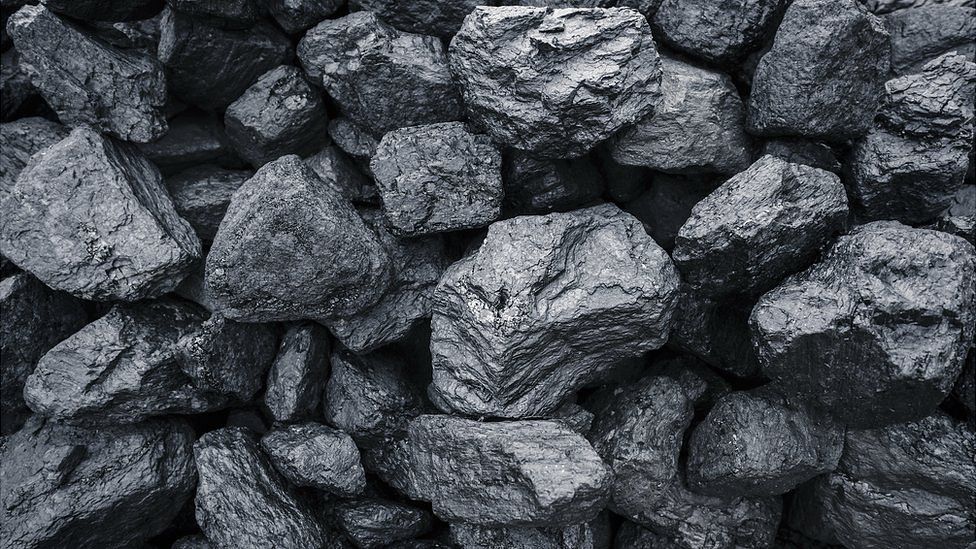
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock composed primarily of carbon, along with various other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Formed from the remains of ancient plants, coal has been a primary source of energy since the Industrial Revolution, with its high energy density and widespread availability making it an attractive fuel for power generation, industrial processes, and domestic heating.
Uses of Coal
The versatility of coal is reflected in its diverse range of applications:
-
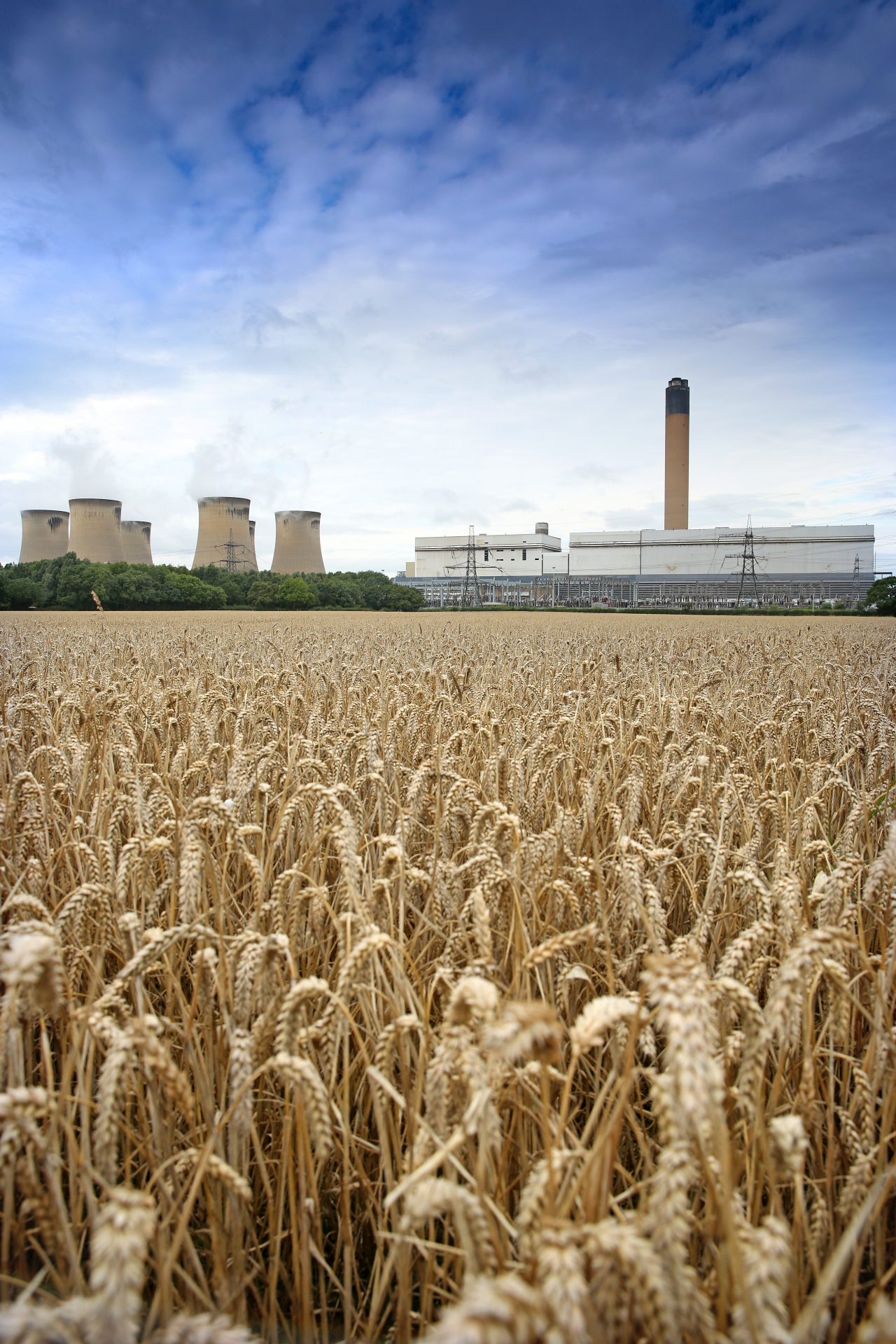
Electricity Generation: Coal is the largest source of electricity worldwide, with coal-fired power plants generating over 37% of global electricity.
-
Industrial Processes: Coal is used in the production of steel, cement, and other industrial processes.
-
Domestic Heating: In many parts of the world, coal is used for cooking and heating homes.
Types of Coal
Coal is classified into four main types based on the carbon content and heat value:
-
Lignite: Also known as brown coal, lignite has the lowest carbon content and is used primarily for electricity generation.
-
Subbituminous Coal: This type has a higher carbon content than lignite and is used for both electricity and industrial processes.
-
Bituminous Coal: With a higher carbon content and higher heat value, bituminous coal is used for electricity generation, industrial processes, and for producing coke for steel production.
-
Anthracite: The rarest and most valuable type, anthracite has the highest carbon content and is used for residential and commercial space heating.
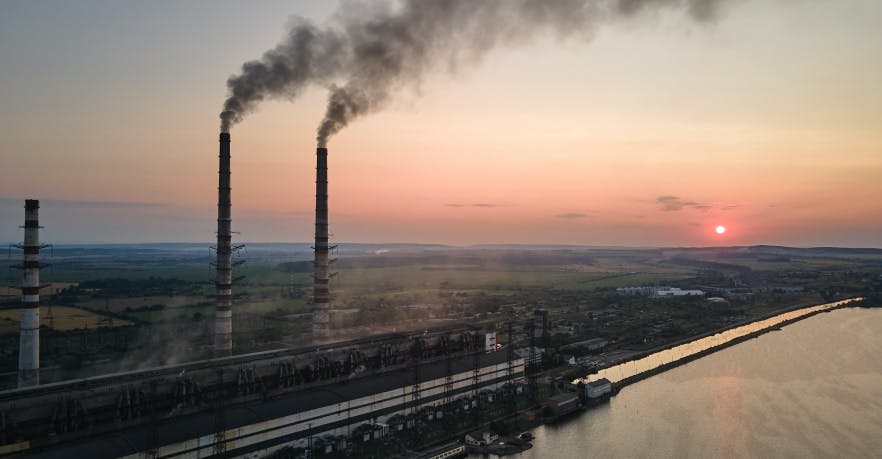
Pollution and Environmental Impact
The extraction, transportation, and combustion of coal have significant environmental and health impacts:
-
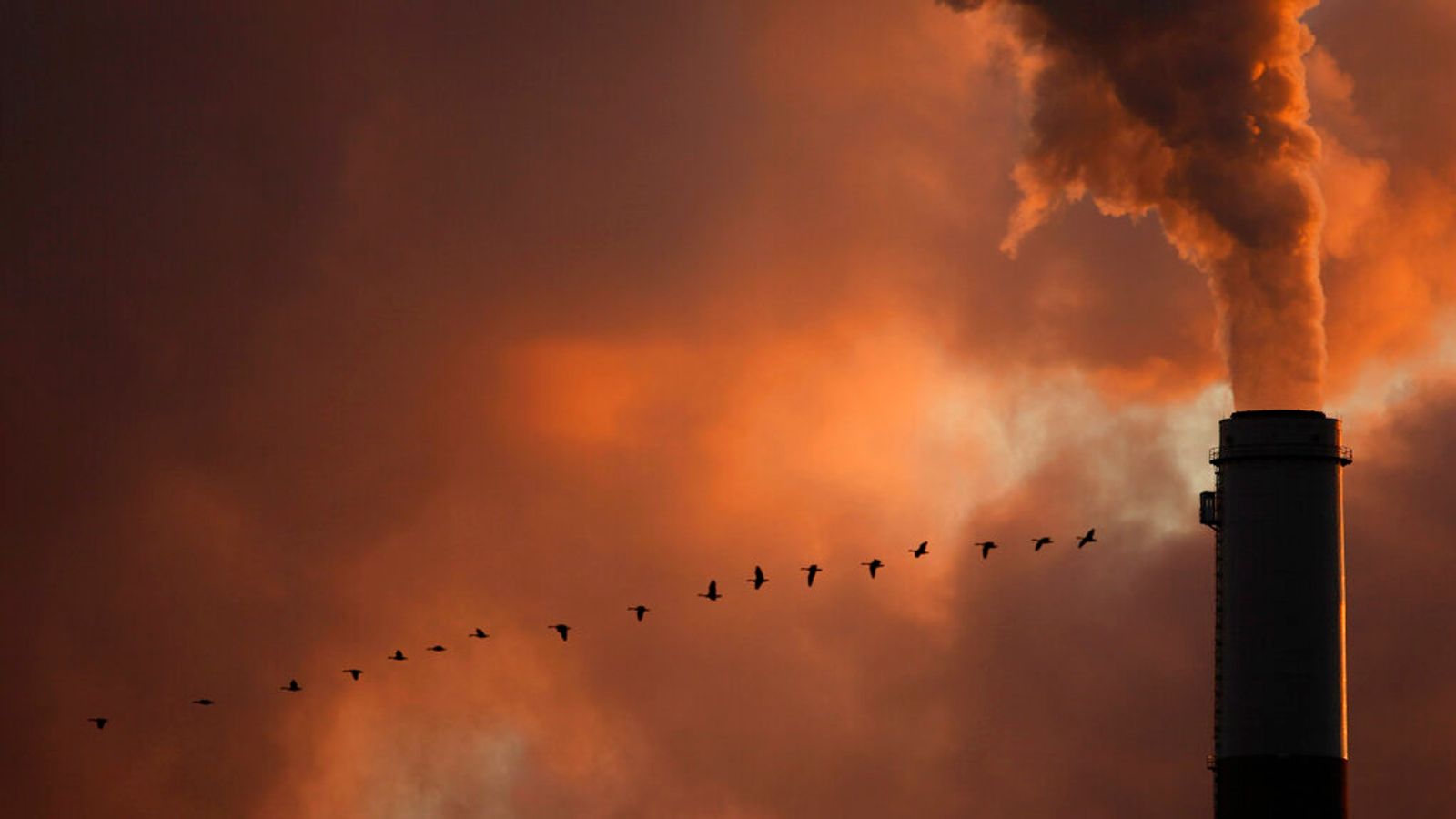
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Coal combustion releases large amounts of carbon dioxide, a major contributor to global warming.
-
Air Pollution: Coal burning releases sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and negative health effects.
-
Water Pollution: Coal mining can lead to water pollution through the release of heavy metals and other pollutants.
Fascinating Facts About Coal
- Coal is the most abundant fossil fuel in the United States.
- The world's largest coal producer is China, accounting for over 50% of global production.
- Coal mining is one of the most dangerous occupations, with thousands of miners losing their lives each year.
Coal, with its complex mix of benefits and drawbacks, presents a challenge for policymakers, industries, and individuals as the world transitions towards cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. While it remains a significant source of energy, efforts to reduce its environmental impact through cleaner coal technologies and the development of renewable energy sources are underway. Understanding the multifaceted nature of coal is crucial for making informed decisions about our energy future and mitigating the adverse effects of coal on the environment and human health.
For more information on coal and other energy topics, visit
Britannica, a leading source of knowledge and education.
By embracing a balanced approach to energy production and consumption, we can work towards a future where energy needs are met without compromising the health of our planet.